Treatments
Treatment for Different Heart Conditions
Click to find out more about each treatment
- Catheter Ablation (Treats heart rhythm problems)
- Implantable Cardiac Devices (Manages heart rhythm abnormality, and/or improve heart function)
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (Non-surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease / angina)
- Coronary Bypass Surgery (Open heart surgery for coronary artery disease and coronary heart disease)
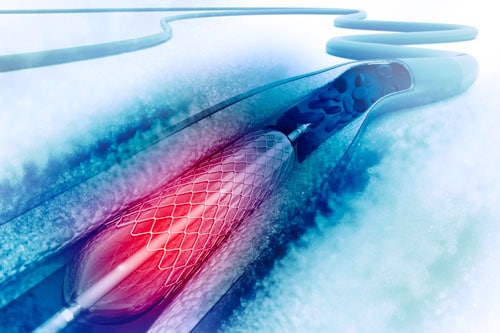
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Also known as Coronary Angioplasty. A non-surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD) / angina, which is a narrowing of the coronary arteries (blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscles).
What To Expect
– A catheter (a thin, flexible tube) is inserted into the blood vessels of the groin or arm to reach your heart.
– Once at the site of the narrowing, a balloon on the tip of the catheter is inflated to enlarge the opening.
– Most often at this point in the procedure, a device called a stent is expanded and left inside the artery to support the opening and prevent further narrowing.
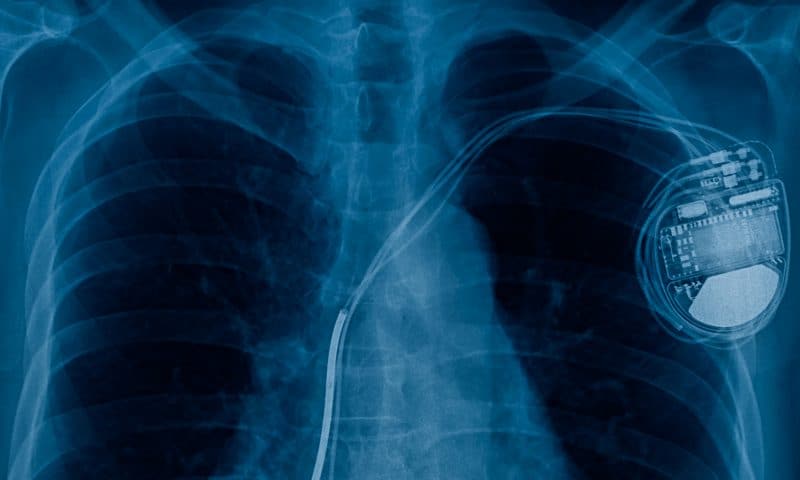
Implantable Cardiac Devices
A category of devices that are implanted in the body of the patient (usually in the left side of the chest near the heart), which help cardiologists to monitor and treat heart rhythm abnormality, and/or improve heart function.
Understanding Different Cardiac Devices
- Permanent Pacemaker Insertion (PPM)
– Treats slow heart rates
– Consists of a battery and electronic circuitry within a metal encasement (the pulse generator), which is connected to the heart via one or more electrode-tipped leads. - Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
– Has similar components as the pacemaker insertion but is larger and designed to treat life
-threatening fast heart beats. - Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy (CRT)
– Has an additional lead that can regulate and improve the pumping action of a heart.
Technological advancements have given rise to PPMs that do not have leads (leadless pacemakers) and ICDs that can be implanted just under the skin with no direct connection to the heart (subcutaneous ICDs).
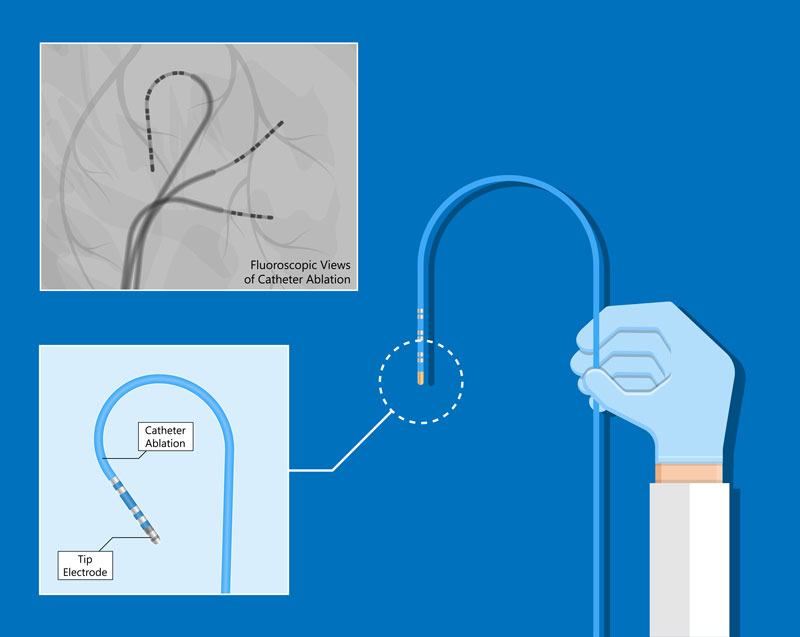
Catheter Ablation
Also known as Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation/Cryoablation (depending on the type of device used). A procedure used to treat heart rhythm problems by selectively destroying areas of the heart that are causing the abnormality.
Ablation can also significantly improve other frequent ectopic conditions such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
What To Expect
Just like in Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) and other percutaneous procedures, catheters are threaded into the heart through tiny holes made on the groin.
- Radiofrequency Ablation
An electrode on the tip of the catheter emits radio-wave energy that destroys the target heart tissue. - Cryoablation
Supercooled fluid pumped through the catheter to a conductive tip is employed to achieve the same effect. For certain conditions such as supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial flutter, ablation may provide a long term cure.
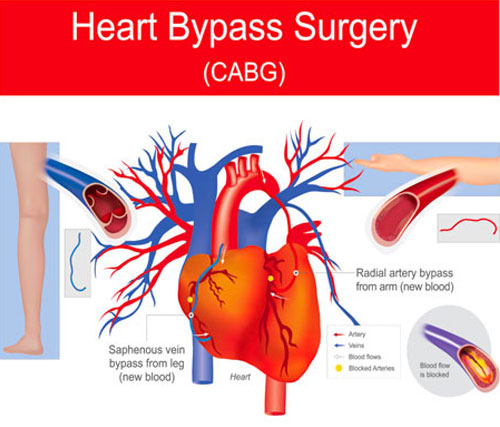
Coronary Bypass Surgery
Also known as Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG), Cardiac Bypass Surgery, Heart Bypass. An open-heart surgery that improves blood flow to the heart muscle, relevant to conditions like coronary artery disease (CAD) and coronary heart disease (CHD), which are closely related.
What To Expect
– A piece of healthy blood vessel is first “harvested” from your leg, arm, or chest, then surgically attached above and below the blockage in the coronary artery.
– Blood flow is then diverted through this section, called the bypass, around the narrowed portion of the diseased artery.
Depending upon the number of blockages, several bypasses may be created, which gives rise to the terms “double-bypass” and “triple-bypass”.
- Category
- Services, Treatments
